Residential Solar: A Smart Investment for Your Home
Introduction to Residential Solar
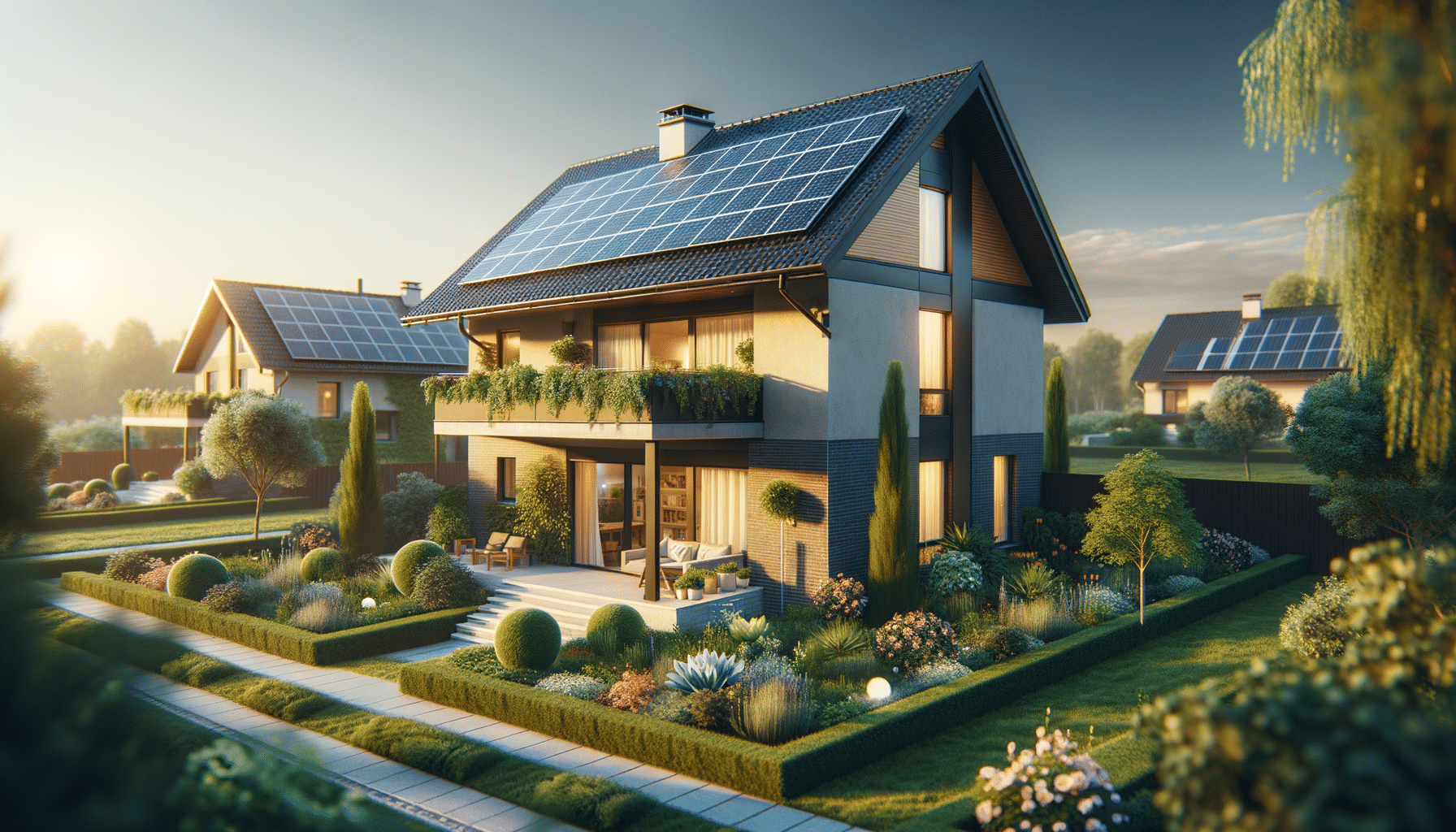
In recent years, the shift towards renewable energy sources has gained momentum, with residential solar power emerging as a pivotal player in this transformation. As homeowners seek sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions, solar energy stands out for its ability to harness the sun’s power, reducing dependency on traditional fossil fuels. Beyond the environmental benefits, residential solar systems offer a practical approach to energy efficiency and financial savings, making them a smart investment for homeowners worldwide.
Understanding How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels, often referred to as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are designed to convert sunlight into electricity. This process involves several key components and steps:
- Photovoltaic Cells: These cells are the heart of the solar panel, made from semiconductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current.
- Inverter: The direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels is converted into alternating current (AC) by an inverter, which is the form of electricity used by home appliances.
- Electrical Panel: The AC electricity is sent to the home’s electrical panel, where it can be used to power lights, appliances, and other devices.
- Net Metering: Excess electricity generated can be fed back into the grid, allowing homeowners to earn credits on their utility bills.
The efficiency of solar panels depends on factors such as the angle of installation, geographic location, and weather conditions. Despite these variables, advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the performance and reliability of solar systems, making them a viable option for many homes.
Financial Benefits of Residential Solar
Investing in residential solar panels can provide substantial financial benefits over time. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Reduced Energy Bills: By generating your own electricity, you can significantly lower or even eliminate your monthly utility bills.
- Incentives and Tax Credits: Many governments offer incentives, rebates, and tax credits to encourage solar adoption, reducing the initial investment costs.
- Increase in Property Value: Homes with solar installations often see an increase in property value, as energy efficiency is a desirable feature for potential buyers.
While the initial cost of solar panels can be high, the long-term savings and potential earnings from surplus energy make it a financially sound decision for many homeowners. Additionally, financing options and leasing programs can help reduce the upfront costs, making solar more accessible.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
One of the most compelling reasons to consider residential solar is its positive environmental impact. Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. By opting for solar power, homeowners contribute to a reduction in carbon footprint and help combat climate change.
Moreover, solar panels have a long lifespan, often exceeding 25 years, with minimal maintenance required. This durability ensures a sustained contribution to environmental conservation over decades, making solar a sustainable choice for the future.
In addition to reducing emissions, solar energy supports energy independence. By generating electricity locally, communities can decrease their dependence on imported fuels, contributing to a more resilient and self-sufficient energy system.
Challenges and Considerations for Homeowners
While the benefits of residential solar are numerous, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing solar panels can be significant, although financing options and incentives can alleviate this burden.
- Space Requirements: Adequate roof space and orientation are crucial for optimal solar panel performance. Shaded or small roofs may not be suitable for installation.
- Weather Dependence: Solar energy production is dependent on sunlight, making it less effective in areas with frequent cloud cover or during shorter daylight hours in winter.
Despite these challenges, many homeowners find that the long-term benefits outweigh the initial hurdles. By carefully evaluating their home’s suitability for solar and exploring available financial options, homeowners can make informed decisions about integrating solar energy into their lives.
Conclusion: Embracing a Solar Future
Residential solar power represents a significant step towards a sustainable and energy-efficient future. By investing in solar technology, homeowners not only reduce their environmental impact but also enjoy financial savings and increased property value. As technology continues to advance and become more affordable, the adoption of solar energy is set to grow, paving the way for a cleaner, greener planet.
For those considering making the switch, assessing your home’s solar potential and exploring financial incentives can provide a clearer picture of the benefits. With the world moving towards renewable energy, residential solar remains a wise and forward-thinking investment.